|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Strength Information Tab |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Strength Information Tab |
  
|
This tab is used to specify the information for the rock specimens.
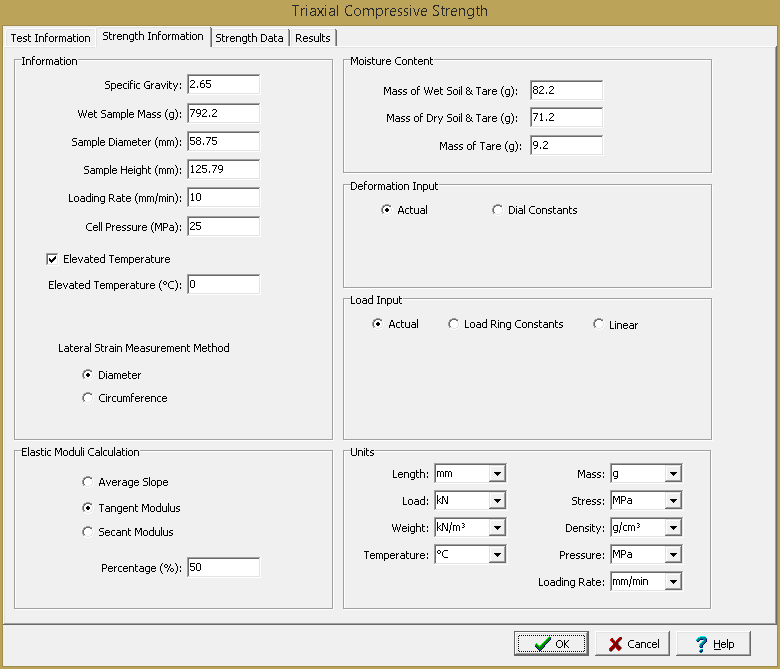
The following can be entered and displayed on this tab:
Information
Water Content: This is used to specify the water content of the sample.
Wet Sample Mass: This is used to specify the mass of the sample, typically at field moisture conditions.
Sample Diameter: This is used to specify the diameter of the cylindrical sample.
Sample Height: This is used to specify the height of the cylindrical sample.
Loading Rate: This is used to specify the loading rate for the test.
Cell Pressure: This is used to specify the cell pressure for the test.
Elevated Temperature: Check this box if the test was performed at an elevated temperature. If the box is checked, the elevated temperature can be specified.
Lateral Strain Measurement Method: This is used to select whether to use the diameter or circumference to calculate the lateral strains.
Elastic Moduli Calculation
The Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio can be calculated using one of the 3 methods below.
Average Slope: This method uses the average slope of the approximately straight line portion of the stress-strain curve.
Tangent Modulus: This method uses the stress level at a fixed percentage (usually 50%) of the maximum strength. If this method is selected the fixed percentage can be specified.
Secant Modulus: This method uses the stress level from zero to a fixed percentage of the maximum strength. If this method is selected the fixed percentage can be specified.
Moisture Content
Mass of Wet Soil & Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the wet soil and tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen.
Mass of Dry Soil & Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the dry soil and tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen.
Mass of Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen.
Deformation Input
The deformations can be specified directly or using deformation dial readings. When using dial readings they are converted to actual deformations using a dial constant.
Actual: Select this to specify the actual deformations on the next tab.
Dial Constant: Select this to specify the dial readings on the next tab and convert them to deformations using a dial constant. When this is selected the Axial Dial Constant and Lateral Dial Constant can be specified. The dial readings will be converted to deformations as described in the calculations section.
Load Input
The axial loads on the next tab can be specified directly or using readings from a load ring. When using readings from a load ring the readings can be converted to axial loads either using load ring constants or a linear equation.
Actual: Select this to enter the axial loads directly on the next tab.
Load Ring Constants: Select this to enter the load ring readings on the next tab and convert them using the method described in the calculations for this test. When this option is selected the Load Ring Constant 1, Load Ring Constant 2, and the Crossover can be specified.
Linear: Select this to enter the load ring readings on the next tab and convert them using the method described in the calculations for this test. When this option is selected the Linear Multiplier and Linear Constant can be specified.
Units
Length Units: This is used to select the units for length.
Mass Units: This is used to select the units for mass.
Loading Rate Units: This is used to select the units for the loading rate.
Force Units: This is used to select the units for force.
Strength Units: This is used to select the units for strength.
Weight Units: This is used to select the units for weight.
Temperature Units: This is used to select the units for temperature.
Pressure Units: This is used to select the units for pressure.
Density Units: This is used to select the units for density.