|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Strength Information Tab |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Strength Information Tab |
  
|
This tab is used to specify the strength information for the soil specimens.
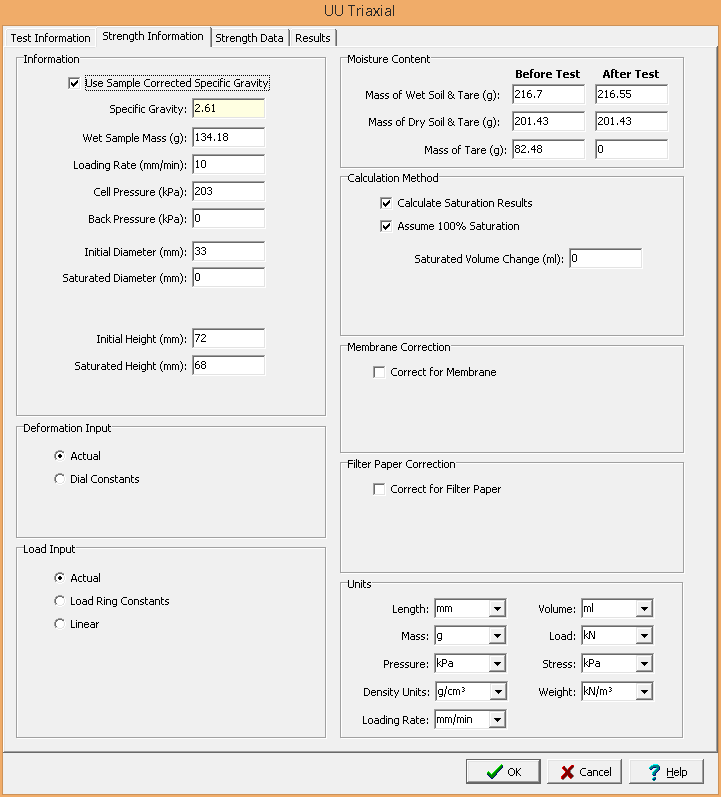
The following can be entered on this tab:
Information
Use Corrected Sample Specific Gravity: The specific gravity can either be specified or determined from a previous specific gravity test. Check this box to use the specific gravity from a previous specific gravity test. If there is no previous specific gravity test for this sample, this box will not be shown.
Specific Gravity: If the User Corrected Sample Specific Gravity box is checked this is the previously determined specific gravity, otherwise this is used to specify the specific gravity to the nearest 0.01 value.
Wet Sample Mass: This is used to specify the mass of the wet sample.
Loading Rate: This is used to specify the loading rate for the test.
Cell Pressure: This is used to specify the cell pressure for the test.
Back Pressure: This is used to specify the back pressure for the test.
Initial Diameter: This is used to specify the initial diameter of the cylindrical sample.
Saturated Diameter: If Calculate Saturation Results is checked, this is used to specify the saturated diameter of the cylindrical sample. If is not specified the saturated diameter will be calculated.
Initial Height: This is used to specify the initial height of the cylindrical sample.
Saturated Height: If Calculate Saturation Results is checked, this is used to specify the saturated height of the cylindrical sample. If is not specified the saturated height will be calculated.
Deformation Input
The lateral and normal deformations can be specified directly or using deformation dial readings. When using dial readings they are converted to actual deformations using a dial constant.
Actual: Select this to specify the actual lateral and normal deformations on the next tab.
Dial Constants: Select this to specify lateral and normal dial readings on the next tab and convert them to deformations using dial constants. When this is selected the Lateral Dial Constant and Normal Dial Constant can be specified. The dial readings will be converted to deformations as described in the calculations section.
Load Input
The axial loads can either be entered directly on the Strength Data tab or determined using load ring readings. When specify load ring readings, if the reading is less than the crossover the axial load = reading * load ring constant 1 and if the reading is higher than the crossover the axial load = (crossover * load ring constant 1) + ((reading - crossover) * load ring constant 2).
Specify Load Ring: Check this box to specify the axial load using load ring readings, otherwise the axial load will be entered directly on the next tab.
Load Ring Constant 1: This is the first load ring constant.
Load Ring Constant 2: This is the second load ring constant.
Crossover: This is the crossover reading between load ring constants.
Moisture Content
Mass of Wet Soil & Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the wet soil and tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen before and after the test.
Mass of Dry Soil & Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the dry soil and tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen before and after the test.
Mass of Tare: This is used to specify the mass of the tare that is used to determine the water content of the specimen before and after the test. If the mass of the tare after the test is not specified it is assumed to be the same as the mass before the test.
Calculation Method
Calculate Saturation Results: Check this box to calculate the saturated water content, void ratio, dry density, wet density and saturation. If this box is checked the saturated height and volume change will be used to calculate saturation properties and stresses.
Assume 100% Saturation: If the Calculate Saturation Results box is checked, this box is used to determine the method used to calculate the saturation properties. If checked the properties are calculated assuming the specimen has been completely saturated during the test. If it not checked the properties are calculated assuming uniform strain (lateral strains are equal to vertical strains).
Saturated Volume Change: If the Calculate Saturation Results box is checked, this is the change in volume of water in the specimen during saturation. It can be determined either by weight changes in the specimen before and after the test or burette readings during the test.The change is positive if the outflow was greater than the inflow.
Membrane Correction
This is used to correct the deviator stress for the effect of the rubber membrane if the error due to the stiffness of the membrane exceeds 5%.
Correct for Membrane: Check this box to apply the correction when the error exceeds 5%.
Membrane Thickness: This is the thickness of the rubber membrane.
Young's Modulus: This is the Young's modulus for the membrane. A typical value for a latex membrane is 1400 kN/m².
Filter Paper Correction
This is used to correct the deviator stress for the effect of the vertical filter paper strips which extend over the total length of the specimen if the error due to the strength of the filter paper strips exceeds 5%.
Correct for Filter Paper: Check this box to apply the correction when the error exceeds 5%.
Perimeter Covered: This is the percentage of perimeter covered by filter paper.
Load Carried: This is the load carried by the filter paper strips per unit length of perimeter covered by filter paper. A typical value for load carried is 0.19 kN/m (1.1 lbf/in.).
Units
Length Units: This is used to select the units for length.
Volume Units: This is used to select the units for volume.
Mass Units: This is used to select the units for mass.
Load Units: This is used to select the units for load.
Pressure Units: This is used to select the units for pressure.
Stress Units: This is used to select the units for stress.
Density Units: This is used to select the units for density.
Weight Units: This is used to select the units for weight.
Loading Rate Units: This is used to select the units for the loading rate.