Understanding how to carry out a thorough penetration test is critical in protecting your organization from unexpected geological conditions. In this guide, we will explore the critical steps behind executing a Standard Penetration Test and how to effectively utilize the data gathered. Armed with practical insights, you will be ready to not only identify potential subsurface challenges but also strategically mitigate risks related to your projects.
Understanding Standard Penetration Testing
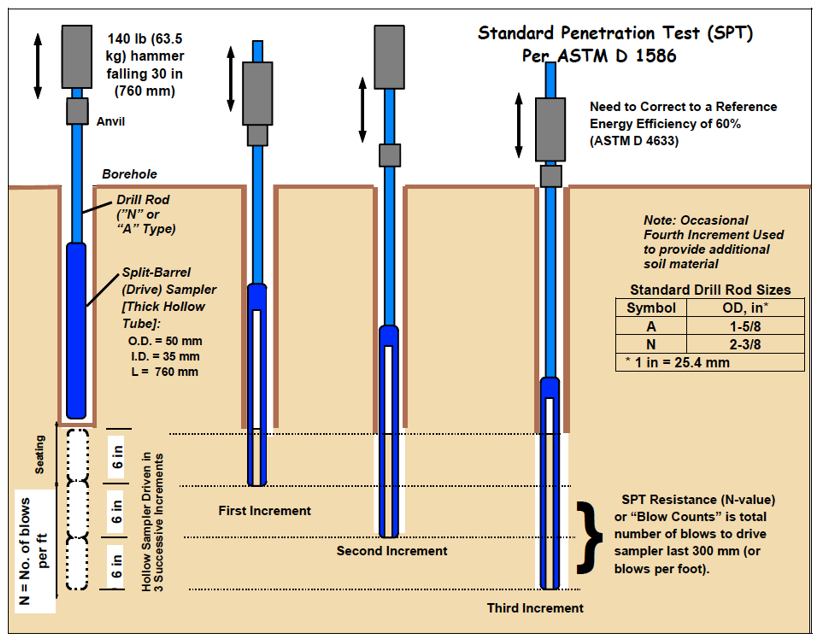
Standard Penetration Testing (SPT) is a commonly utilized in-situ test implemented to gauge the physical properties of soils. This test involves driving a hollow sampling tube into the ground using a predetermined weight in a specified number of blows. The results obtained can indicate various aspects of soil structure, density, and strength, which play a pivotal role in design decisions in engineering projects. Understanding the rationale behind SPT is fundamental for professionals in fields such as geotechnical engineering, construction, and environmental consulting.
Purpose of Standard Penetration Test
The SPT is conducted primarily to ascertain:
- Soil Density: The number of blows required to drive the samplings tube a certain distance provides insight into the compaction and density of the soil.
- Soil Consistency: Variations in the number of blows may reflect differences in soil types, indicating if adjustments in construction techniques or designs are needed.
- Bearing Capacity: The SPT results can assist in estimating the bearing capacity of the soil, which is crucial when assessing whether the soil is adequate to support structures.
- Soil Stratification: Understanding how different layers of soil interact can impact drainage, stability, and excavation processes.
Preparing for a Standard Penetration Test
1. Site Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right site is pivotal. Ensure that the location is safe and accessible. Terrain, environmental constraints, and proximity to existing structures must all be considered. Prepare the site by clearing any debris that could obstruct the tests.
2. Equipment Setup
Necessary equipment includes:
- Standard Penetration Test Hammer
- Hollow Sampling Tubes
- Measuring Equipment
- Safety gear (hard hats, gloves)
Set up the equipment according to the specifications, ensuring that all calibration is conducted correctly.
3. Personnel Training
It is essential to ensure that all staff involved in the SPT have received adequate training in both the technical execution of the test and the adherence to safety protocols to mitigate the risk of accidents.
Conducting the Standard Penetration Test
Now we will detail the step-by-step procedure to conduct an SPT effectively:
Step 1: Equipment Calibration
Before any test, verify that all measuring devices are functioning correctly. Calibrate your equipment to avoid inaccurate results during the testing process.
Step 2: Executing the Test
- Positioning the Sample Tube: Place the hollow sample tube at the designated location, ensuring it is vertical and evenly positioned.
- Driving the Tube: Use the hammer to drive the tube into the ground. The effective test typically consists of driving the tube a total depth of about 18 inches. Record the number of blows required to penetrate the first foot and the subsequent feet.
Step 3: Data Recording
After conducting the test:
- Document the total number of blows required for each foot of penetration.
- Note any variations in soil type encountered during the test.
- Capture the depth of refusal noted during the testing process.
Step 4: Sample Collection
Carefully extract the sample tube once the SPT is complete. Ensure that you keep soil samples intact for later laboratory testing.
Interpreting SPT Data
After conducting the Standard Penetration Testing, accurate interpretation of test results is essential to make informed decisions regarding construction and project planning.
1. Analyzing Blow Count
The blow count recorded during the test is used to determine the soil’s relative density, which can help categorize it into three classifications:
- Loose (N < 4): Implies the soil may be weak and prone to instability.
- Medium Dense (N = 4-10): Indicates moderate strength and suitable bearing capacity.
- Dense (N > 10): Suggests high load-bearing capabilities and stability.
2. Correlating SPT Results with Other Parameters
SPT results can be correlated with other geotechnical parameters such as
- Cohesion Coefficient: Determines the strength of the soil matrix.
- Internal Friction Angle: Analyzing where soil experiences shear failure is vital.
- Foundation Design: Employing a comprehensive understanding can guide the design process of foundations, thus ensuring the safety of future structures.
Real-World Applications of SPT Data
Utilizing data from Standard Penetration Tests can immensely influence project outcomes across diverse sectors:
- Civil Engineering: SPT data is used to assess soil behavior under loading, which helps in the development of stable foundations for bridges and high-rises.
- Environmental Engineering: Identify contamination risks through soil stratification and data obtained via SPT to decide remediation measures.
- Civil Infrastructure: Projects like roadways, railways, and utility installations rely heavily on understanding soil competency, making SPT invaluable.
Best Practices in Using SPT Data
1. Accurate Documentation
Ensure that all data collected during the SPT is accurately documented. Use advanced techniques in data logging to minimize human error.
2. Collaboration Across Disciplines
Engage with other professionals such as civil engineers, environmental consultants, and geologists to accurately interpret the implications of SPT data. Collaboration ensures that comprehensive assessments are made, leading to improved project outcomes.
3. Re-evaluation of Existing Data
Review information acquired from previous SPTs when planning new projects. Historical data can provide insights into potential geological issues, reducing costs and ensuring safety.
Keeping Safety in Mind
Safety should not be compromised during Standard Penetration Testing. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are critical to minimizing risks and facilitating operational success.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Ensure all personnel wear adequate PPE, including helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots to protect against injuries.
2. Site Safety Protocols
Maintain strict safety guidelines around heavy machinery and ensure the site is monitored for environmental stability to avoid accidents.
Technology Integration in SPT
Advancements in technology continually enhance the quality and efficiency of Standard Penetration Testing:
- Data Collection Software: Use of specialized software can streamline data analysis, improving quick decision-making.
- 3D geological modeling: Helps visualize soil behavior under various conditions, supplementing the data obtained from SPT for a holistic understanding.
Conclusion: How to Leverage Your Knowledge
The Standard Penetration Test is a fundamental tool in geotechnical engineering that provides critical insights into soil properties. Incorporating the findings from your SPT not only assists in making informed design choices but significantly impacts safety.
Headline: ## Mastering Standard Penetration Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Did you know that properly conducting a Standard Penetration Test can save your business from catastrophic failures and financial losses? Understanding how to carry out a thorough penetration test is critical in protecting your organization from unexpected geological conditions. In this guide, we will explore the critical steps behind executing a Standard Penetration Test and how to effectively utilize the data gathered. Armed with practical insights, you will be ready to not only identify potential subsurface challenges but also strategically mitigate risks related to your projects.
Understanding Standard Penetration Testing
Standard Penetration Testing (SPT) is a commonly utilized in-situ test implemented to gauge the physical properties of soils. This test involves driving a hollow sampling tube into the ground using a predetermined weight in a specified number of blows. The results obtained can indicate various aspects of soil structure, density, and strength, which play a pivotal role in design decisions in engineering projects. Understanding the rationale behind SPT is fundamental for professionals in fields such as geotechnical engineering, construction, and environmental consulting.
Purpose of Standard Penetration Test
The SPT is conducted primarily to ascertain:
- Soil Density: The number of blows required to drive the samplings tube a certain distance provides insight into the compaction and density of the soil.
- Soil Consistency: Variations in the number of blows may reflect differences in soil types, indicating if adjustments in construction techniques or designs are needed.
- Bearing Capacity: The SPT results can assist in estimating the bearing capacity of the soil, which is crucial when assessing whether the soil is adequate to support structures.
- Soil Stratification: Understanding how different layers of soil interact can impact drainage, stability, and excavation processes.
Preparing for a Standard Penetration Test
1. Site Selection and Preparation
Choosing the right site is pivotal. Ensure that the location is safe and accessible. Terrain, environmental constraints, and proximity to existing structures must all be considered. Prepare the site by clearing any debris that could obstruct the tests.
2. Equipment Setup
Necessary equipment includes:
- Standard Penetration Test Hammer
- Hollow Sampling Tubes
- Measuring Equipment
- Safety gear (hard hats, gloves)
Set up the equipment according to the specifications, ensuring that all calibration is conducted correctly.
3. Personnel Training
It is essential to ensure that all staff involved in the SPT have received adequate training in both the technical execution of the test and the adherence to safety protocols to mitigate the risk of accidents.
Conducting the Standard Penetration Test
Now we will detail the step-by-step procedure to conduct an SPT effectively:
Step 1: Equipment Calibration
Before any test, verify that all measuring devices are functioning correctly. Calibrate your equipment to avoid inaccurate results during the testing process.
Step 2: Executing the Test
- Positioning the Sample Tube: Place the hollow sample tube at the designated location, ensuring it is vertical and evenly positioned.
- Driving the Tube: Use the hammer to drive the tube into the ground. The effective test typically consists of driving the tube a total depth of about 18 inches. Record the number of blows required to penetrate the first foot and the subsequent feet.
Step 3: Data Recording
After conducting the test:
- Document the total number of blows required for each foot of penetration.
- Note any variations in soil type encountered during the test.
- Capture the depth of refusal noted during the testing process.
Step 4: Sample Collection
Carefully extract the sample tube once the SPT is complete. Ensure that you keep soil samples intact for later laboratory testing.
Interpreting SPT Data
After conducting the Standard Penetration Testing, accurate interpretation of test results is essential to make informed decisions regarding construction and project planning.
1. Analyzing Blow Count
The blow count recorded during the test is used to determine the soil’s relative density, which can help categorize it into three classifications:
- Loose (N < 4): Implies the soil may be weak and prone to instability.
- Medium Dense (N = 4-10): Indicates moderate strength and suitable bearing capacity.
- Dense (N > 10): Suggests high load-bearing capabilities and stability.
2. Correlating SPT Results with Other Parameters
SPT results can be correlated with other geotechnical parameters such as
- Cohesion Coefficient: Determines the strength of the soil matrix.
- Internal Friction Angle: Analyzing where soil experiences shear failure is vital.
- Foundation Design: Employing a comprehensive understanding can guide the design process of foundations, thus ensuring the safety of future structures.
Real-World Applications of SPT Data
Utilizing data from Standard Penetration Tests can immensely influence project outcomes across diverse sectors:
- Civil Engineering: SPT data is used to assess soil behavior under loading, which helps in the development of stable foundations for bridges and high-rises.
- Environmental Engineering: Identify contamination risks through soil stratification and data obtained via SPT to decide remediation measures.
- Civil Infrastructure: Projects like roadways, railways, and utility installations rely heavily on understanding soil competency, making SPT invaluable.
Best Practices in Using SPT Data
1. Accurate Documentation
Ensure that all data collected during the SPT is accurately documented. Use advanced techniques in data logging to minimize human error.
2. Collaboration Across Disciplines
Engage with other professionals such as civil engineers, environmental consultants, and geologists to accurately interpret the implications of SPT data. Collaboration ensures that comprehensive assessments are made, leading to improved project outcomes.
3. Re-evaluation of Existing Data
Review information acquired from previous SPTs when planning new projects. Historical data can provide insights into potential geological issues, reducing costs and ensuring safety.
Keeping Safety in Mind
Safety should not be compromised during Standard Penetration Testing. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are critical to minimizing risks and facilitating operational success.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Ensure all personnel wear adequate PPE, including helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots to protect against injuries.
2. Site Safety Protocols
Maintain strict safety guidelines around heavy machinery and ensure the site is monitored for environmental stability to avoid accidents.
Technology Integration in SPT
Advancements in technology continually enhance the quality and efficiency of Standard Penetration Testing:
- Data Collection Software: Use of specialized software can streamline data analysis, improving quick decision-making.
- 3D geological modeling: Helps visualize soil behavior under various conditions, supplementing the data obtained from SPT for a holistic understanding.
Conclusion: How to Leverage Your Knowledge
The Standard Penetration Test is a fundamental tool in geotechnical engineering that provides critical insights into soil properties. Incorporating the findings from your SPT not only assists in making informed design choices but significantly impacts safety.
Are you ready to ensure your projects are underpinned with solid geological understanding and reliable data? Take full advantage of your findings and consider integrating modern data management solutions into your workflow to enhance safety and efficiency.